SOILS OF KERALA
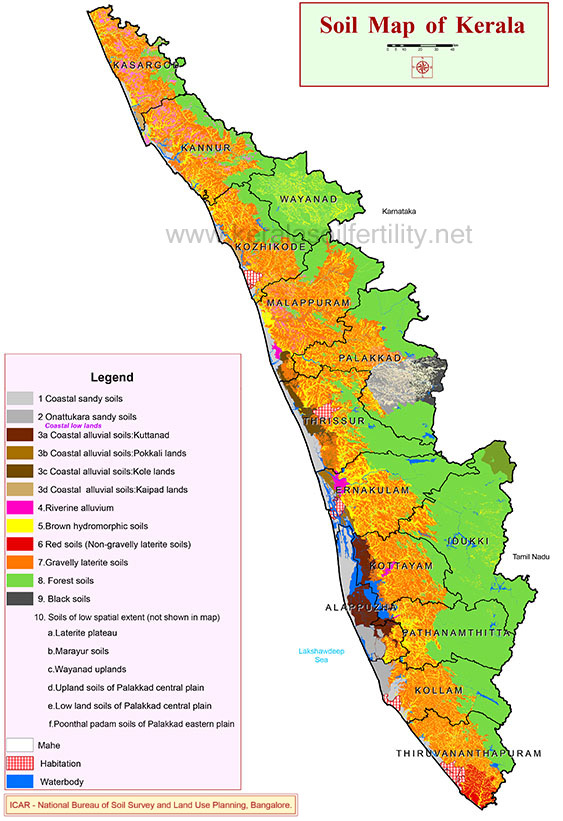
Kerala State, a narrow strip of land along the coast is
located in the extreme south western part of the Indian
peninsula. It is flanked by the Lakshadweep Sea on the west
and the lofty mountains of the Western Ghats on the east.
The state enjoys a hot humid tropical climate with two
distinct monsoons viz. the south west and the north east. The
mean annual rainfall for the last 10 years (2007-2016)
recorded is 2790 mm with mean maximum and minimum temperature
of 32°C and 23°C respectively.
Historically the state
is covered by a tropical ever green forest climax vegetation
with marshes in the lowlands and mangroves in the coastal
lowlands. Physiography is characterized by a combination of
distinct altitudinal variations resulting from the rise of the
land mass from 5 m below sea level in the west to the soaring
heights of 2695 m in the east. Three distinct parallel
physiographic zones viz; low land, mid land and high land have
been identified.
The parent materials of most of the
soils of the state are the weathering products of crystalline
acidic rocks, sedimentary formations and recent and sub recent
sediments. The dominant soil forming process is laterisation
which is an intense rock weathering process. Local variations
in climate, vegetation and relief have a modifying effect on
the factors of soil formation leading to the development of a
variety of soils.
The nomenclature adopted for the different
kinds of soils described in this section is a combination of
landforms, local place names and in some instances soil
properties. Taxonomic equivalents for these soils are
available in a number of publications. Ten broad soil groups
and salient features
COASTAL SANDY SOILS (COASTAL PLAINS)

Distribution
Coastal areas of Thiruvananthapuram, Kollam, Alappuzha,
Ernakulam, Thrissur, Malappuram, Kozhikode, Kannur and Kasaragod
districts
General features
Sandy soils of marine origin. Deep and well drained. Low in
organic matter, deficient in plant nutrients. Low capacity to
retain water and nutrients
Fertility characteristics
Acidic, low to medium in organic carbon, high available
phosphorus, low in potassium, magnesium and boron
Land use
Rice in the lowlands and vegetables during summer Coconut and
tuber crops in uplands
ONATTUKARA SANDY SOILS (ONATTUKARA PLAINS)
Distribution
Kollam and Alappuzha districts
General features
Sandy soils, very deep, well drained, low in organic matter,
deficient in plant nutrients. Sea water intrusion in coastal
areas
Fertility characteristics
Acidic, poor in available nutrients and bases. High P levels in
soils. Salinity is a problem in coastal areas.
Land use
Rice in the lowlands and vegetables during summer Coconut and
tuber crops in uplands
COASTAL ALLUVIUM (POTENTIAL ACID SULPHATE SOILS- COASTAL LOWLANDS)

Distribution
Occur in coastal lowlands in areas slightly below or above sea
level in Alappuzha, Kottayam and Ernakulam districts
General features
Soils formed from river alluvium and sulphur rich marine
sediments and are potential acid sulphate. They are extremely
acidic and poorly drained. Salinity problem in coastal areas
Fertility characteristics
Extremely acidic, high level of organic matter, low P, deficient
in calcium, magnesium and boron
Land use
Rice is the major crop, vegetables grown during summer months in
upper reaches. Coconut and tuber crops in raised bunds
Integrated farming system with components on livestock and
fisheries are successfully practiced in some areas.
POKKALI SOIL

Distribution
Occur in coastal lowlands in areas slightly below or above sea
level in Alappuzha, Ernakulam, and Thrissur districts
General features
Soils formed from river alluvium and sulphur rich marine
sediments and are potential acid sulphate. Soils are extremely
acidic and poorly drained. Salinity problem in coastal areas.
Fertility characteristics
Extremely acidic, clayey, high levels of organic matter and
phosphorus, deficient in calcium, magnesium and boron
Land use
Rice is the major crop followed by fish culture, Saline
resistant ‘Pokkali’ variety is cultivated in mounds to overcome
salinity hazards The monsoon rains wash away the salts from the
mounds which are removed by tidal action. Fertilizers are not
usually recommended
KOLE SOIL

Distribution
Occur in coastal lowlands in areas slightly below or above sea
level in Thrissur and Malappuram districts
General features
Soils formed from river alluvium and sulphur rich marine
sediments and some areas along the coast are potential acid
sulphate. Soils are fertile and poorly drained. Salinity is a
problem in coastal areas.
Fertility characteristics
Extremely acidic, high levels of organic matter and P, deficient
in calcium, magnesium and boron
Land use
Rice is the major crop, vegetables during summer months in upper
reaches. Coconut and tuber crops in raised bunds
KAIPPAD SOIL
Distribution
Occur in coastal areas slightly above sea level in Kannur
District
General features
Soils formed from river alluvium and sulphur rich marine
sediments and are potential acid sulphate. Soils are extremely
acidic and poorly drained. Salinity problem in coastal areas.
Fertility characteristics
Extremely acidic, high levels of organic matter and P, deficient
in calcium, magnesium sulphur, copper and boron
Land use
Rice is the major crop saline resistant varieties cultivated,
vegetables during summer months in upper reaches. Coconut and
tuber crops in raised bunds
RIVERINE ALLUVIAL SOILS (RIVER BANKS)

Distribution
Along the river banks in all the districts
General features
Very deep, acidic, well drained, non gravelly with varying
texture(sandy loam to clay loam) formed from river alluvial
deposits
Fertility characteristics
Acidic, medium in organic matter and potassium, high in
phosphorus and deficient in Magnesium and boron
Land use
Rice in low lands Coconut, tuber crops, banana and vegetables in
uplands
BROWN HYDROMORPHIC SOIL
Distribution
Foot hills and valleys of the midland laterite terrain of all the
districts
General features
Acidic, deep, poorly drained, deficient in plant nutrients with
toxic level of iron.
Fertility characteristics
Acidic, low to medium in organic matter, high phosphorus, low
potassium, deficient in calcium, magnesium and boron
Land use
Rice is the major crop followed by tuber crops, banana and
vegetables. Coconut in raised bunds
RED NON GRAVELLY LATERITE SOIL

Distribution
Southern parts of Thiruvananthapuram District
General features
Very deep, non gravelly, acidic, well drained, clayey red soils.
Absence of plinthite layer in lower layers
Fertility characteristics
Acidic, medium in organic matter, phosphorus and potassium.
Adequate in calcium, magnesium and sulphur. Deficient in copper
and boron
Land use
Coconut is major crop followed by banana, tuber crops,
vegetables Rice is grown in lowlands
GRAVELLY LATERITE SOIL

Distribution
Midland terrain of all the districts
General features
Gravelly, well drained, strongly acidic, low water retention
capacity, high phosphorus fixation, poor in bases. Good physical
properties, but prone to erosion. Hard laterite pan in lower
layers restricting root penetration
Fertility characteristics
Strongly acidic, high available phosphorus, deficient in
magnesium and boron
Land use
Coconut, Banana, vegetables, rubber, tuber crops Rice is grown
in lowlands
FOREST SOIL

Distribution
Forest areas in all the districts
General features
Non gravelly, deep, well drained, acidic, loamy or clayey, rich
in organic matter. Soils are reddish brown to dark brown, sub
soils are clay loam to clay texture.
Fertility characteristics
Moderately acidic, high in organic matter, low in phosphorus,
adequate in secondary and micro nutrients
Land use
Mostly forested areas
BLACK SOIL

Distribution
Occur in nearly level plains of Chittoor Taluk in Palakkad
District
General features
Alkaline reaction, deep, non gravelly, high activity clay soils
with shrink-swell behavior, saturated with bases and contains
free calcium carbonate. Moisture deficit experienced for five
months. Soils exhibit cracking on the surface during summer and
poor workability.
Fertility characteristics
Alkaline reaction, low organic matter and available phosphorus,
adequate in secondary and micro nutrients except boron
Land use
Rice in lowlands Coconut, vegetables, tuber crops and banana in
raised bunds
SPECIAL GROUP (SOILS OF LIMITED SPATIAL EXTENT)
Five special soil groups have been identified. These soils are distributed in patches and are of limited spatial extent.
The salient features of these soils are given below.
Laterite plateau
Malappuram, Kozhikode, Kannur and Kasaragod districts
Very shallow soils formed by severe erosion and exposure of
plinthite layer found in nearly level plateau on the top of
undulating hills. Exposed laterite forms iron stone by
irreversible hardening Shallow soils, Not suitable for
crop cultivation
Marayoor soil (Lowhills and rolling lands)
Marayoor, Vattavada and Kanthalloor panchayats of Idukki
District Deep, near neutral, well drained, loamy, non
gravelly soils, well supplied with plant nutrients
Slightly acidic soils, medium organic matter, high phosphorus,
adequate in secondary and micro nutrients except boron
Mostly forested Cool season fruits & vegetables, potato and
sugarcane are cultivated
Wayanad upland soil
Uplands of eastern parts of Wayanad District Near
neutral, red, deep, well drained, loamy or clayey and well
supplied with bases Slightly acidic, medium in organic
matter, phosphorus, potassium and deficient in boron
Coffee, tea, arecanut and pepper in uplands. Rice and banana in
lowlands
Upland soils of Palakkad central plains
Alathur, Kuzhalmannam, Nenmara Blocks and western parts of
Chittoor Taluk in Palakkad District Near neutral or
slightly acid, red, deep, non gravelly loam or clay, moderate
nutrient and water holding capacity Slightly acid to
slightly alkaline, medium in organic matter, phosphorus,
potassium and deficient in boron Coconut is the main
crop with intercrops of tuber crops, banana and vegetables Rice
in the lowlands
Low land soils of Palakkad central plain
Lowlands of Alathur and Chittoor Blocks, Palakkad taluk and
Palakkad municipality Moderately acid, deep,
imperfectly drained, loam or clay, well supplied with bases.
Moderate capacity to hold nutrients and water Slightly
acid, medium in organic matter, phosphorus, potassium and
deficient in boron Rice is the major crop
Poonthal padams (Lowlands of Palakkad eastern plains
Lowlands of Chittoor taluk in Palakkad District Slushy
soils with poor workability. Near neutral in reaction, base rich
fertile clayey soils and imperfectly drained Neutral
reaction, medium in organic matter and deficient in boron
Rice is the major crop
Contact Us
+ 91 471 2527567, + 91 471 2700777

© 2019 | System conceived,designed and implemented by IIITMK


